
Diamond Guide
A trusted guide to understanding the beauty, value, and true quality of diamonds, so you can choose with confidence what shines forever.
The 4Cs
Diamond Cut
The cut is the design and craftsmanship within the stone that brings out the light, causing it to reflect in fire, brilliance, and sparkle. The cut consists of the stone’s shape and proportion, which are made up of:
- Symmetry
- Polish
- Cut
The combination of these three aspects results in the stone’s overall cut grade.

Diamond Clarity
The clarity of a diamond is based on the number, size, and location of its
internal and external inclusions. These are typically observed with a 10x
magnifying lens and are generally not visible to the naked eye. Inclusions
are seen as natural fingerprints rather than imperfections.
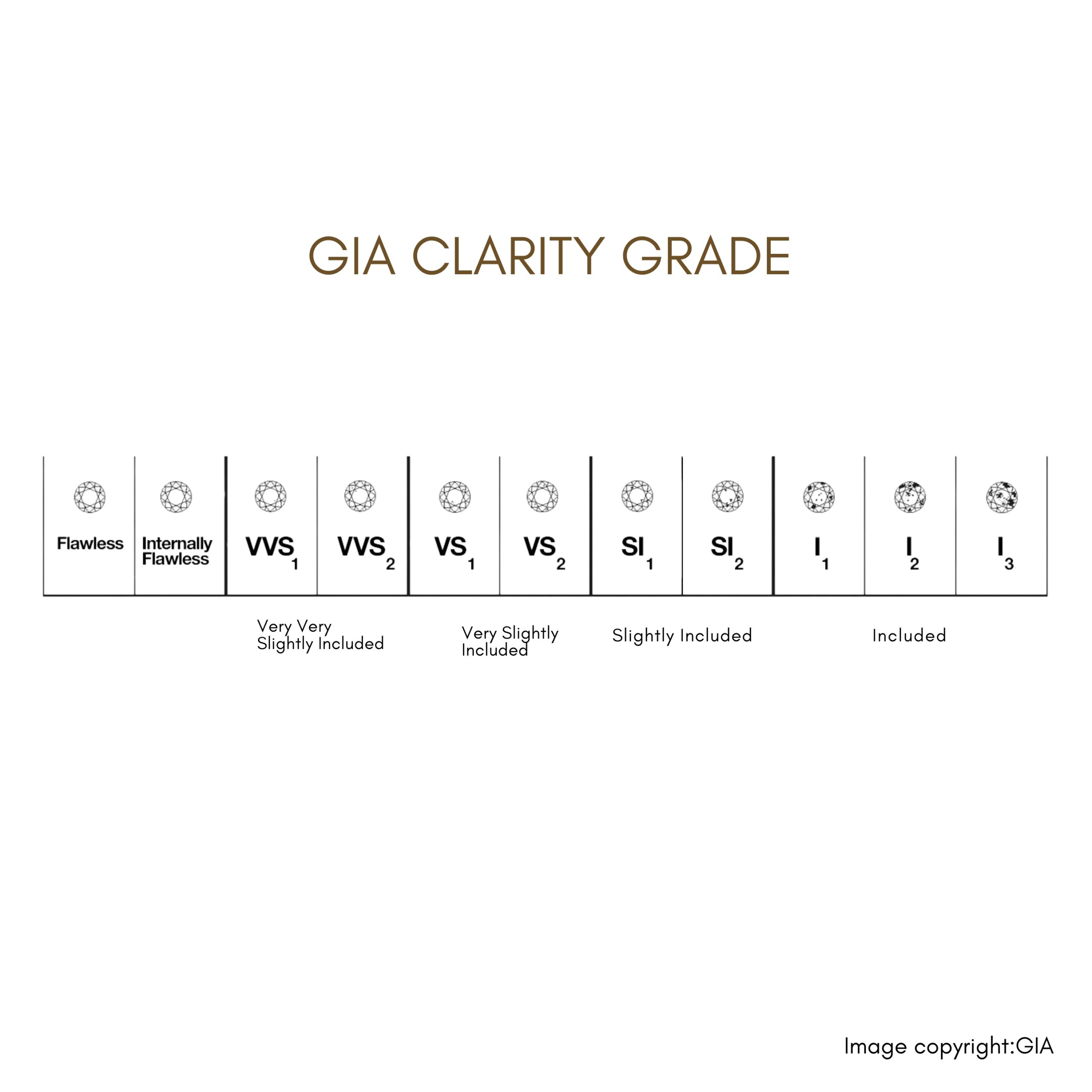
Clarity grades are as follows:
Flawless (FL): No internal or external blemishes
VVS1: Very, very slightly included with one small inclusion far from the
centerVVS2: Very, very slightly included with two small inclusions far from the
centerVS1: Very slightly included with one inclusion closer to the center
VS2: Very slightly included with two inclusions closer to the center
I1, I2, I3: Included with 1, 2, or 3 inclusions in the center of the diamond,
and this is the only grade visible to the naked eye
Diamond Color
Diamonds are found in 27 color combinations, with the category of colorless diamonds being the most popular.
Colored diamonds are much rarer than colorless ones, though they are not always more expensive. Colorless diamonds are graded from D (colorless) to Z (yellowish tint).
Color is considered the second most important feature when selecting a diamond because, after size, it’s the most noticeable characteristic at first glance. In transparent diamonds, a color grade indicates the presence or absence of a yellowish tint in the stone.

Diamond Carat
Carat is the weight measurement of a diamond. When choosing a diamond, carat may serve as a guide or informative detail, but it should not be the sole determining factor.
Carat does not necessarily indicate the diamond’s actual size, as it more accurately reflects the proportions, which are key to defining the stone’s mass.


Rings Size Guide
Find a ring, possibly a ‘band’ type ring, which is exactly your size. Choose your size by placing the ring on the sheet: the inside diameter of the ring should match the diameter of one of the circles.
Use a ruler or a caliper to measure the inside diameter of the ring and find the equivalent diameter of one of the circles. For example, if your ring has an inside diameter of 16.6 mm, this will correspond to size 52. If the diameter falls between two sizes, choose the larger size.
Remember to measure your size at room temperature. Your fingers will usually be slightly smaller in the winter than in the summer – cold fingers in the winter – warm fingers in the summer.